Hearing loss in children
Hearing loss in children can effect speech development
Hearing loss in children, whether short term or long term, may have a big effect on speech development, language and therefore learning. To learn to speak for the first time we must be able to hear all of the parts of the word to understand the meaning and reproduce the sounds. Hearing loss in children disrupts the learning process for speech.
Hearing loss in children services in New Zealand
Children in New Zealand are screened for hearing loss soon after birth, in the newborn hearing screening program, usually, while they are still in the hospital. Children who do not pass the screening assessments are referred to Audiologists for a full assessment.
Children who are found to have permanent hearing loss are fitted with hearing aids or cochlear implants as soon as possible to give them the best chance of developing speech and language. Most of the assessment and habilitation for young children is done for free within the hospital system.
Types of hearing loss in children
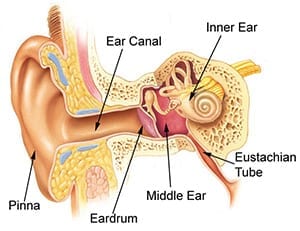
Sensorineural hearing loss occurs due to a problem in the inner ear (cochlear) or in the higher auditory pathways. Usually, this type of hearing loss is permanent.
A conductive hearing loss in children occurs when the sound is blocked from getting to the inner ear. This type of hearing loss could be temporary or permanent.
Auditory process in disorder (APD) occurs in the higher sound processing area of the brain. Children with APD have normal peripheral hearing.
Otitis media is an accumulation of fluid in the middle ear. This fluid stops the eardrum and the small middle ear bone from moving freely and therefore causes a conductive hearing loss (resistance of sound) moving through the middle ear space.
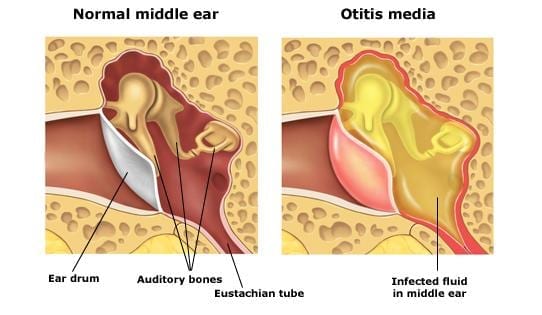
Acute Otitis Media – is often painful and last around 3 weeks before resolving its self.
Chronic Otitis Media – means fluid remains in the middle ear space over a long period of time. Some children may not experience (or show pain).
The fluid that remains for a longer period of time becomes more viscous and “gluey”…hence the name glue ear.
Glue ear causes a significant hearing loss and if not resolved does affect the development of speech and there for language and learning.
Auditory Processing Disorder
Auditory Processing Disorder (APD) is a hearing problem which occurs not in the ears but in the hearing pathways or hearing centres of the brain. The ears may process sound normally, and the person may pass ordinary hearing tests, but the brain has difficulty interpreting what is heard. This type of hearing loss adversely affects understanding, especially in difficult listening situations such as when there is another distracting sound present, or when listening to complex information or instructions. As a result, learning is usually affected.
SoundSkills is a centre based in Greenlane Auckland that specialises in the assessment and habitation of APD. If you are concerned that your child may have APD we will do the initial hearing assessment here at Auckland hearing and then refer you on to SoundSkills (other Audiologist the specials in APD).
Hearing Assessment for Children
Every manufacturer offers devices at various technology levels. The features on the inside of hearing aids are what reflects the price you pay, not what the hearing aids look like on the outside. The top end technology hearing aids have all the premium features and suit people with high listening needs. Lower technology (and priced) hearing aids have less sophisticated features and will work well in quieter listening environments. There are many hearing aids styles, and most of them are available at each level of technology. Learn more about hearing aids here.
The hearing aid price categories described below give you a feel for how hearing aids are classified. Please call the clinic for more details of these price ranges.
Paediatric hearing assessment at Auckland Hearing
To learn to speak for the first time we must be able to hear all of the parts of the word to understand the meaning and reproduce the sounds. Hearing loss disrupts the learning process for speech. Hearing assessments for children are often called paediatric hearing tests. This link will take to a “Hearing Health Check” for children and adults on the New Zealand Audiological Society (NZAS) website.
Testing children’s hearing
Testing babies and small children
Automatic testing – Auditory brainstem response testing is used for babies up to a few months old. While the baby sleeps a clicking sound is played through headphones and electrodes that have been placed on the babies head measure electrical brain signals. This test becomes more difficult as children get older as they must be asleep for the test.
Visual reinforcement Audiometry – Is a behavioural test and can be done from when the baby sits on the caregiver’s knee and can turn their head (a few months old). A sound is played to one side of the child, when they turn their head toward it a puppet is showed to them in the window.
Older Children
Play Audiometry – is used for children of about 3 to 6 years old. They listen to sounds through headphones than put a peg in a board or a similar game.
Older children – will do a hearing test in a similar way to adults by pressing a button or tapping when they hear a sound.
Immittance Audiometry or middle ear testing involves putting a small plug into the ear and increasing the pressure slightly. This measures whether the eardrum is moving and therefore whether is fluid in the middle ear space.
If there is fluid, then the eardrum will not move. This test also picks up if there is a hole in the eardrum or a patent (working) grommet. This is a quick accurate and painless test for both children and adults.
Tests according to age
Testing younger children’s hearing (0 to 3 years)
Automatic testing – Auditory brainstem response testing is used for babies up to a few months old. While the baby sleeps a clicking sound is played through headphones and electrodes that have been placed on the babies head measure electrical brain signals. This test becomes more difficult as children get older as they must be asleep for the test.
Visual reinforcement Audiometry – Is a behavioural test and can be done from when the baby sits on the caregiver’s knee and can turn their head (a few months old). A sound is played to one side of the child, when they turn their head toward it a puppet is showed to them in the window.
Younger children must be seen at a centre where there are 2 specialist paediatric audiologists and a room set up.
Children 0 – 5 years can be seen at the Auckland University – School of Audiology in Glen Innes. They sometimes have free appointments for children. Call (09) 923 9909 for an appointment.
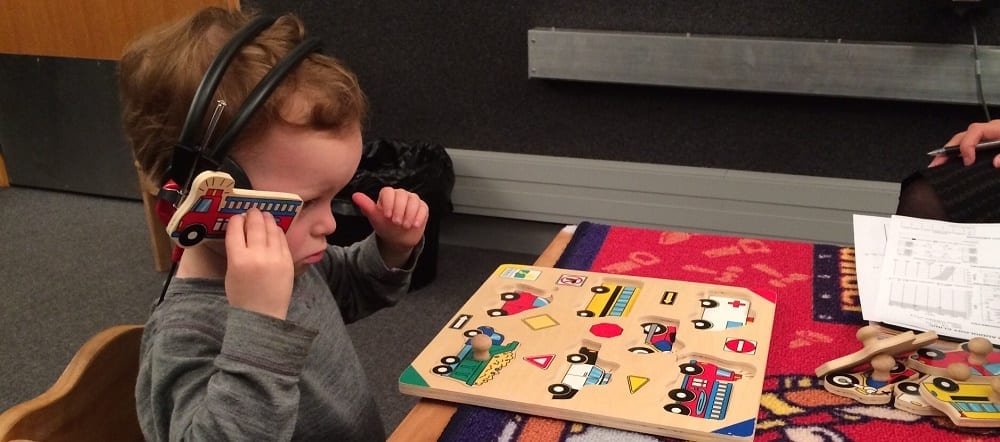

Hearing assessments for children – 3 and 4 years old (testing not done at Auckland Hearing)
Speech testing – (Kendall toy test) Children are asked to identify objects or pictures when they are presented (spoken) at very quiet levels.
Play Audiometry – is used for children of about 3 to 4 years old and sometimes older. They listen to sounds through headphones then respond by putting a peg in a board or a similar game.
Older children – will do a hearing test in a similar way to adults by pressing a button or tapping when they hear a sound.
Hearing Assessment Children over 5 years old
Paediatric hearing assessment will identify hearing loss in children. We see children over the age of five for full hearing assessments; including testing includes pure tone audiometry, speech perception testing and middle ear assessments.
- A hearing assessment for children will take 30 – 60 minutes, we will set aside 1 hour for the appointment.
Hearing aids – If hearing aids are required children are usually referred to the free hospital service. We are able to fit hearing aids to children at Auckland Hearing if preferred, the cost of the hearing aids are covered by the government (for New Zealand residents) but you will need to pay for the appointments.
Auditory Processing Disorder (APD)– Children with normal peripheral hearing but who are showing signs of Auditory Processing difficulties will be referred on for further assessment. Soundskills require a normal hearing assessment before seeing children (preferably 7 years or over) for further testing. We do the initial hearing assessments for children here at Auckland Hearing.


